
title: specify the label you want to add.The parameters used above are described below: The syntax to add a legend to the plot: (, ncol=1, loc="upper left", bbox_to_anchor=(1,1)) We use the () method to mark out and label the elements of the graph. We can add a legend to the plot using the matplotlib module. Generate a Plot: Use the show() method to visualize the plot on the user’s windows.Add Legend: By using the legend() method we can add a legend to a plot.Plot scatter graph: By using the scatter() method we can draw a plot.Define X and Y: Define the data coordinates values used for the x-axis and y-axis.Defining Libraries: Import the important libraries which are required for data creation and manipulation ( Numpy and Pandas) and for data visualization ( pyplot from matplotlib).The following steps are used to plot scatter graph and add a legend to it are outlined below: It represent the reletionship between two variables in a data-set. Scatter Plot is a graph in which the values of two variables are plotted along two axes. Legendis an area that outlines the elements of the plot.
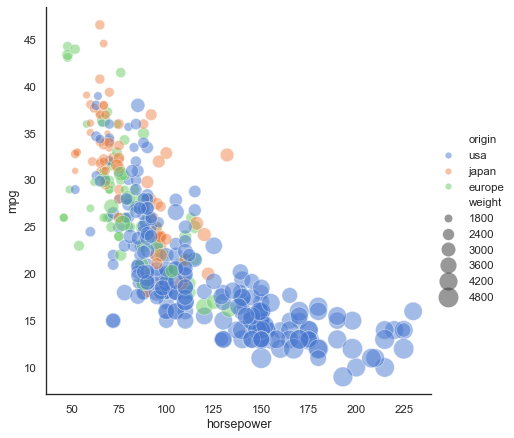
Now before starting the topic firstly, we have to understand what does “legend” means and how “scatter plot created”.
#Matplotlib scatter marker size legend how to
In this section, we learn about how to add a legend to the Scatter Plot in matplotlib in Python.
#Matplotlib scatter marker size legend full
If “auto”,Ĭhoose between brief or full representation based on number of levels. If “full”, every group will get an entry in the legend. Variables will be represented with a sample of evenly spaced values. Specified order for appearance of the style variable levels You can pass a list of markers or a dictionary mapping levels of the Setting to True will use default markers, or Object determining how to draw the markers for different levels of the Normalization in data units for scaling plot objects when the Otherwise they are determined from the data. Specified order for appearance of the size variable levels, Which forces a categorical interpretation. List or dict arguments should provide a size for each unique data value, sizes list, dict, or tupleĪn object that determines how sizes are chosen when size is used. Or an object that will map from data units into a interval. hue_norm tuple or Įither a pair of values that set the normalization range in data units Specify the order of processing and plotting for categorical levels of the

Imply categorical mapping, while a colormap object implies numeric mapping. String values are passed to color_palette(). Method for choosing the colors to use when mapping the hue semantic. Grouping variable that will produce points with different markers.Ĭan have a numeric dtype but will always be treated as categorical. Grouping variable that will produce points with different sizes.Ĭan be either categorical or numeric, although size mapping willīehave differently in latter case. Grouping variable that will produce points with different colors.Ĭan be either categorical or numeric, although color mapping willīehave differently in latter case. Variables that specify positions on the x and y axes. Either a long-form collection of vectors that can beĪssigned to named variables or a wide-form dataset that will be internally Parameters : data pandas.DataFrame, numpy.ndarray, mapping, or sequence This behavior can be controlled through various parameters, asĭescribed and illustrated below. In particular, numeric variablesĪre represented with a sequential colormap by default, and the legendĮntries show regular “ticks” with values that may or may not exist in theĭata.

Represent “numeric” or “categorical” data. Semantic, if present, depends on whether the variable is inferred to The default treatment of the hue (and to a lesser extent, size) Hue and style for the same variable) can be helpful for making Using all three semantic types, but this style of plot can be hard to It is possible to show up to three dimensions independently by Parameters control what visual semantics are used to identify the different Of the data using the hue, size, and style parameters. The relationship between x and y can be shown for different subsets scatterplot ( data = None, *, x = None, y = None, hue = None, size = None, style = None, palette = None, hue_order = None, hue_norm = None, sizes = None, size_order = None, size_norm = None, markers = True, style_order = None, legend = 'auto', ax = None, ** kwargs ) #ĭraw a scatter plot with possibility of several semantic groupings.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
